Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Banking

It seems that people still associate blockchain mainly with BitCoin and other cryptocurrencies, while the potential of this technology goes far beyond that. We have already written about the opportunities it brings to logistics, healthcare, gambling, and the public sector. In this blog post, we want to speak about the advantages of blockchain in banking.
Blockchain in Various Industries – Key Stats
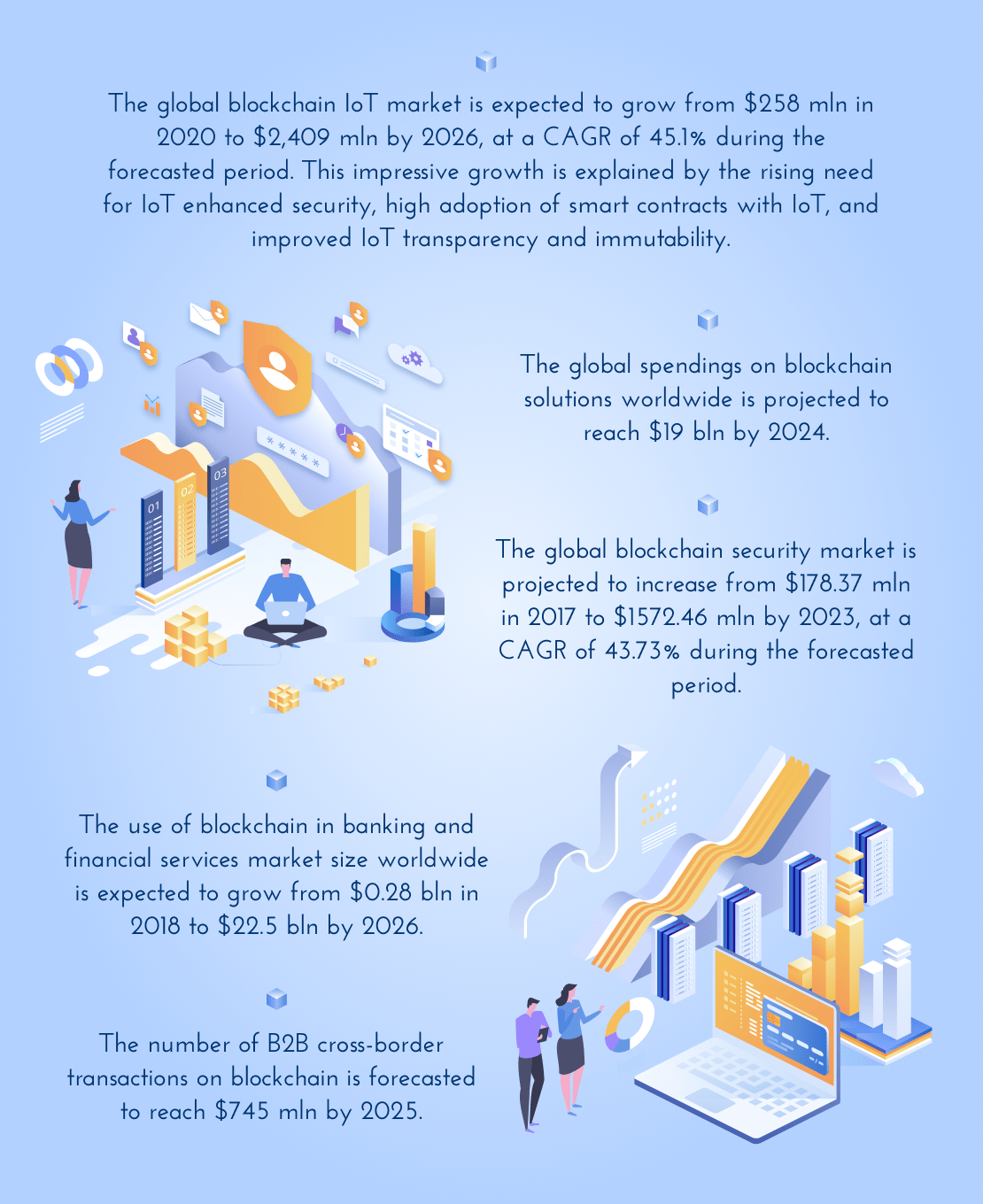
Source : scand.com
What Is Blockchain in Banking?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that holds encrypted blocks of records with all the digital transactions performed by blockchain users. When blockchain is used as a business network, it allows its participants to record their transactions and track them in the system. The recorded transactions can’t be removed from the block or modified. This way, blockchain helps its users to make banking processes more secure, reliable, transparent, and efficient.
This technology enhances data protection, making it immutable and easy to verify. It can drive data security across various industries to a brand new level, eliminating fraud and mistakes. Since the banking industry suffers the most from scammer attacks, implementing blockchain in financial services may save the day. Here are the core pros of blockchain in banking:
Security
Use of blockchain in banking allows businesses to cover a range of security issues. The technology can be implemented at different levels from protecting sensitive records to enhanced user authentication. Here is how blockchain can improve security in digital banking systems:
- User authentication – blockchain eliminates the necessity to protect user and bank accounts and devices with passwords. Instead, the technology combines blockchain security with biometrics, encrypting users’ unique identifiers e.g. iris scans, fingerprints, voice, etc. into a block in blockchain. The technology uses the encrypted block with user identifiers as an access key to apps and gadgets or as a key to sign the data the user sends to others.
- Data protection – due to the decentralized nature of blockchain, cyber criminals have to work with an entire blockchain system rather than a central node to hack it. Since the data is spread across multiple nodes, there is no particular server or another place to attack. For this reason, some banking institutions use blockchain for data storage and securing transactions.
- Secure communication – blockchain can be used for securing internal communication, preventing any data leakages or cyber espionage. The technology spreads the metadata utilized for communications around the distributed ledger, making it impossible for hackers to collect it at one centralized point.
Speed
Today, many banking operations and financial transactions are rather slow and can take much time for their management, approval, and logging, moreover, some actions are still performed manually. Fintech blockchain easily solves that issue allowing instantaneous authentication and verification which helps to streamline banking processes e.g. performing quick cross-border payments, finance trading, KYC verification, etc., and reduce paperwork.
What’s more, with a unified blockchain-based platform across banking institutions, banks can provide an uninterrupted operation of finance services. Therefore, making their work more efficient and improving their customers’ digital banking experiences.
Transparency
Blockchain technology in banking increases transaction transparency, making it easy to detect and prevent fraud. As banks use a shared digital ledger for recording each transaction, it increases their visibility for the blockchain participants. Therefore, banks can easily track the history of each transaction and verify it. This way, blockchain banking leaves no place for money laundering, scam, and other fake operations.
Decentralization
Another outstanding blockchain feature important for the financial sphere is decentralization. Decentralization leads to a more democratic relationship in the market between individuals and institutions. Instead of relying on a central authority that controls every transaction, buyers and sellers can directly communicate with each other. This results in lower operational costs, increased trust between transactors, and the inability of individuals or separate organizations to control the market.

Source : scand.com
For example, international payments in decentralized digital currencies are cheaper in comparison to transnational fiat payments as they eliminate any bank fees and don’t conform to any bank policies. Moreover, decentralized currencies are more resistant to destabilized currency rates as they aren’t regulated by any national monetary policies, representing a more stable alternative.
Smart Сontracts
Smart contracts are blockchain programs that self-execute once certain conditions are met. This blockchain technology can facilitate many processes in banks and financial institutions. Here is how banks can use smart contracts in their work:
- automate insurance claims – smart contracts can automatically validate the claims indicated in the contracts and execute them once all or certain requirements are met;
- reduce operational costs – as smart contracts are self-regulatory they don’t require much manual intervention, as a result, financial institutions can lower their transaction costs in the long term;
- automate money transfers – with smart contracts financial institutions can process payments and transfer funds in real-time;
- perform simple auditing – traditional contracts require manual processing, meaning additional workforce and lengthy audit process; smart contracts, in their turn, support diverse bookkeeping tools which facilitate contract processing.
With blockchain-based smart contracts, banking and financial institutions can significantly reduce the level of bureaucracy, ensure trust between partners, accelerate processes as well as decrease the need for third-party intermediaries.
Blockchain in Finance: Use Cases
Now let us take a look at more specific cases of how blockchain can change the banking and finance industry.
Improved KYC
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a procedure of identity verification performed by banks each time they get a new customer. Today it might take over a month as there is a need for getting reviews and approvals from third-party organizations and other banking institutions. Each year banks spend up to $ 160 million on KYC compliance.
The implementation of fintech blockchain is an effective solution that accelerates the verification process, eliminates mistakes and duplications, prevents multiple interactions with a range of institutions as well as allows avoiding fraud and forgery. Once verified, the data will be securely stored within the system and easily provided to other banks (strictly in case of necessity).
Direct Payments and Lendings
At the same time, blockchain financial services allow peer-to-peer or company-to-company direct payments without banks and processing centers as intermediaries. The transactions get faster and cheaper, blockchain also ensures traceability and transparency — this brings the world to the concept of DeFi (Decentralized Finance). The idea of DeFi is that everyone across the globe can easily participate in a new financial ecosystem that allows peer-to-peer lending and payments, avoiding the necessity to use the services of banks, lending companies, and other institutions. So, along with the benefits, blockchain also has some risks for banks and may cause the need for changes in their processes.
Global Trade Finance
Being implemented into the financial system, blockchain can significantly improve and optimize global trade processes and supply chain management. With the help of smart contracts and blockchain-based IoT solutions, the companies involved in the international trading network can effectively regulate mutual financial liabilities, verify the quality of goods, trust each other more, make all the necessary payments — and all of these will require less time, money, and effort.
Clearance and Settlements Systems
Blockchain distributed ledger technology can facilitate and speed up bank transfers. A usual bank transfer from one part of the world to another can take up to 3 days. This happens as the transfer has to pass a sophisticated system of intermediaries comprising correspondent banks and custodial services. The banks that perform the sending and receiving transfer procedures, in their turn, have to align with the global financial system that includes various traders, asset managers, funds, and much more.

Source: scand.com
Blockchain technology in banking can remove the necessity to reconcile each transaction across many financial institutions’ ledgers. Instead, each financial institution has access to the same distributed ledger with registered transactions. This way, each transaction is public, transparent, and unified to each participant in the entire network of custodial services and correspondent banks.
Fundraising
Traditional fundraising through venture capital can be a rather challenging and time-consuming process. Companies have to work on two fronts – searching for outside investors and working on their product development. Blockchain ICOs disrupt conventional fundraising concepts allowing companies to raise funds much faster and in a shorter-circuit process.
Companies create their own initial coin offerings (ICOs) which they sell to the public via famous cryptocurrency platforms like Ethereum or BitCoin. This way, they can quickly raise the necessary funds even before launching their product to the market.
Being a new fundraising method, ICOs are currently barely regulated. Nevertheless, many businesses see the potential of ICOs and experiment with them. David Pakman, a former partner at Venrock, who is currently working at crypto VC firm CoinFund says that crypto “seems to be the largest and most interesting opportunity for long term venture investment, wealth creation, and disruption.”
Source : scand.com



